Russia and China’s increasing influence in Arctic Region
- Posted By
10Pointer
- Categories
World Affairs
- Published
3rd Sep, 2022
-
-
Context
In lieu of trade and economic sanctions by US and EU on Russia amid Russia-Ukraine war, China and Russia’s negotiations and meeting over Arctic region draws discussions all around the world.
-
Background
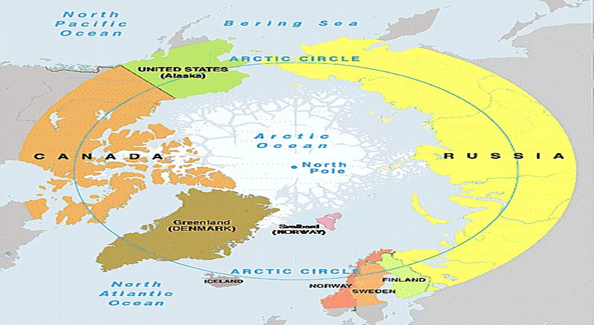
- The Russian Federation has always maintained a stronghold in Arctic politics due to its vast geography, relatively large population in the region amongst the littoral states, longest coastline and powerful stature in world affairs.
- The melting Arctic connects North America, Asia, and Europe creating new sea routes.
- The region contains 30 per cent of the gas and 16 per cent of total oil resources on the planet.
- The presence of natural resources makes the Arctic a new geopolitical hotspot with the increase in global energy demands.
Who governs Arctic region?
- The Arctic Council is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic.
- The Arctic Council works as a consensus-based body to deal with issues such as the change in biodiversity, melting sea ice, plastic pollution and black carbon.
Russia’s Interest in the region:
- Initiating ties with China: The economic sanctions by the Western states are prompting Russia to enhance its ties with the People’s Republic of China.
- Pretend to be saver of Arctic region: Russia declares that it wants to safeguard the Arctic as a zone of peace and cooperation.
- To Strengthen Trade: It aims to use the Northern Sea Route as a national integrated transport system.
China’s emerging Interests:
- Increase Trade opportunities: China is trying to find ways to reduce the length of its trade routes and avoid the disputed passageways like the Strait of Malacca whilst maintaining energy sufficiency.
- On Resource in the region: China issued its first ever white paper on the Arctic in 2018. The first Arctic-sourced liquefied natural gas (LNG) was delivered to China. Russia and China have cooperated effectively on LNG projects since then.
- The Yamal Peninsula, inside the Arctic, is the site of the first ever Polar Silk Road cooperation between the two states.
- Against West: Besides that, it can also serve strategic purposes amid the Sino-US and Russo-US rivalries.
- In Exploration activities: China inaugurated the Yellow River Scientific Research Station in Svalbard. In 2013, China got observer status in the Arctic Council.
-
- The Arctic Council is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic.
- The Arctic Council works as a consensus-based body to deal with issues such as the change in biodiversity, melting sea ice, plastic pollution and black carbon.
-
Analysis
What are the points of discussion among the Parties of Arctic council?
- The recent invasion of Ukraine by Russia has resulted in worsening prospects for the Russian economy in the wake of economic sanctions imposed by the US and the EU.
- The Kingdom of Denmark, Canada, Iceland, Finland, Sweden, Norway, and the US have issued a joint statement against the Russian aggression in Ukraine calling it a grave impediment to cooperation in the Arctic as well.
- They have refused to attend the meetings under the chairmanship of Russia and have paused the participation in the Arctic Council and the subsidiary bodies. This move greatly isolates Russia in the region.
India’s Aspirations of Arctic
|
India launched its first scientific expedition to the Arctic Ocean in 2007 and opened a research base named "Himadri” at the International Arctic Research Base at Ny-Alesund, Svalbard, Norway in July 2008 for carrying out studies in disciplines like Glaciology, Atmospheric sciences & Biological sciences.
|
- To study the hypothesized tele-connections between the Arctic climate and the Indian monsoon by analysing the sediment and ice core records from the Arctic glaciers and the Arctic Ocean.
- To characterize sea ice in the Arctic using satellite data to estimate the effect of global warming in the northern polar region.
- To conduct research on the dynamics and mass budget of Arctic glaciers focusing on the effect of glaciers on sea-level change.
- To carry out a comprehensive assessment of the flora and fauna of the Arctic and their response to anthropogenic activities. In addition, it is proposed to undertake a comparative study of the life forms from both the Polar Regions
What can be the implication on India by increased Sino-Russia cooperation?
- Militarization of Arctic: Russia is involved in the militarization of the Arctic. It is placing hypersonic ballistic missiles that can threaten the US.
- Polarisation of major Trade partners for India: Russia and China both are major trade partners to India. The sanctions by US and Europe have already made difficulties for Indian imports from the region.
- Increasing China’s Influence: China expanded its scope till west, east, South and even North to India, which is strategically not beneficial for our country.
- Territorial proximity of Russia & China: As compared to other western countries, Russia and China holds geographic proximity to India, which can cause threat to security.
-
Way forward
- Global Cooperation and Multilateralism is the way out for all to better management of Arctic.
- Environment is to be saved and parties should rather invest on its betterment, and not on their single interests.
-
Conclusion
For China, Russia is the biggest “Gatekeeper of the Arctic” and a necessary partner. With growing energy demands, China sees the Russian Far East, Siberia, and Russian Arctic as sources of energy resources, export markets, trading routes, and recipients and partners on infrastructure and other developmental projects.
The Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavov called China the priority partner to Russia in the Arctic by which he meant the Russian Arctic only. China is now seeking more managerial positions within the Arctic. It has stressed on the governance of the Arctic and reciprocity.

