UN’s Population Division has released 2022 edition of World Population Prospects on World Population Day, i.e., on 11July.
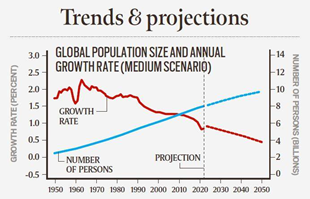
What is World Population Prospects?

|
Net flow of labours:
|

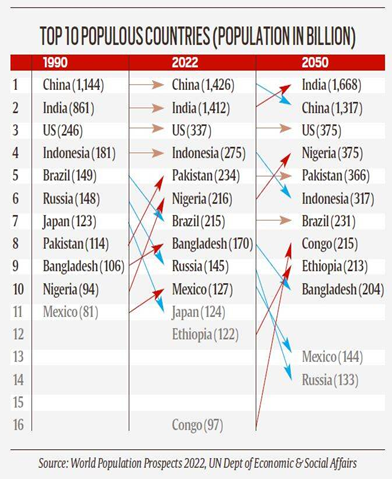
The increase in old age aged population is growing quite fast and its faces several challenges, social security is one of the big challenge. The demographic dividend needs to be perished with skill development and education to sustain the increasing dependency ratio.
Verifying, please be patient.