Introduction
Horticulture is a branch of agriculture that deals with the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and herbs. Horticulture is mainly concerned with the growing and management of plants that are used as sources of food and also for medicinal and aesthetic purposes. It is the process of garden cultivation using scientific methods to generate fruits, vegetables, and flowers in larger quantities and varieties. The horticulture sector is considered one of the leading sectors of agriculture in various parts of the world. India is in the path of developing its Horticulture sector, but this is also evident that every growth is associated with the major challenges if not managed properly, Like the Green Revolution for Rice and Wheat.
Origin and Evolution of Horticulture
- The history of horticulture overlaps with the History of agriculture and
- The origins of horticulture lie in the transition of human communities from a nomadic lifestyle as hunter-gatherers to sedentary, or semi-sedentary, horticultural communities.
- In the Pre-Columbian Amazon Rainforest, natives used biochar to enhance soil productivity by smoldering plant waste.
- European settlers called this soil ‘Terra Preta de Indio’. In forest areas, such horticulture was often carried out in "slash and burn" areas.
- In pre-contact North America, the semi-sedentary horticultural communities of the Eastern Woodlands, who grew maize, squash, and sunflower, contrasted markedly with the nomadic hunter-gatherer communities of the Plains people.
Horticulture in India
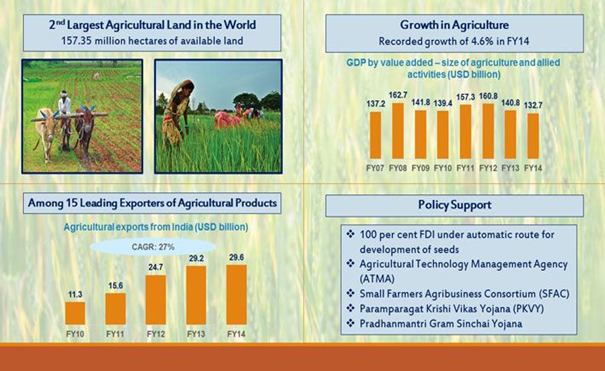
- In India, the major part of horticulture production comprises fruits and vegetables. India has a highly favourable climate for agro products such as fruits, vegetables, spices, and aromatic plants.
- The horticulture sector in India produces around 320 million tons of products and contributes about 33% of the Gross Value Addition (GDA).It is a labour-intensive sector and thus provides a lot of employment opportunities, especially for the people of rural regions.
- The innovative and advanced techniques adopted in horticulture have increased production and export opportunities resulting in more growth. In India, 10% of the land in horticulture contributes to 33% of Agricultural Value.
- Over the years, the horticulture sector has emerged as a prominent contributor to overall economic development.
- India has favourable geographical features that help in the growth of a variety of vegetables. More than 40 types of vegetables are grown in different parts of India. India ranks second in the production of vegetables worldwide.
- Fruit production in India constitutes more than 10 per cent of the world’s production.
- Indian states like Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka have the major share of fruit production.
- The favourable climatic conditions facilitate the production of a variety of flowers throughout the year in selected regions of the country. The growing demand for flowers among the upper and middle classes for beautification purposes has helped in the growth of floriculture as a well-developed business.
Types of Horticulture practices in India
There are several major areas of focus within the science of horticulture.
They include:
- Olericulture: the production of vegetables.
- Pomology, also called fruticulture: the production of fruits and nuts.
- Viticulture: the production of grapes (largely intended for winemaking).
- Floriculture: the production of flowering and ornamental plants.
- Turf management: the production and maintenance of turf grass for sports, leisure and amenity use.
- Arboriculture: the cultivation and care of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants, primarily for landscape and amenity purposes.
- Landscape horticulture: the selection, production and care of plants used in landscape architecture.
- Postharvest physiology: the management of harvested horticultural crops to retard spoilage while stored or transported.
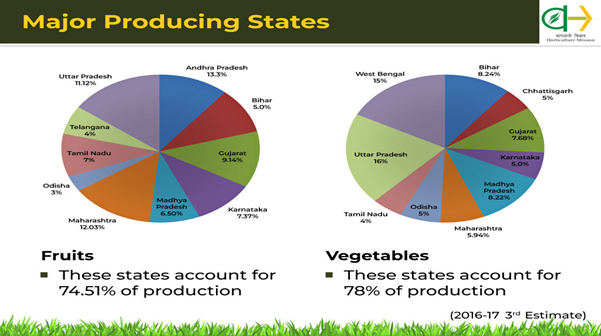
Present Situation- Growth of Horticulture in India
- Recently, Department of Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmers Welfare released the Third Advanced Estimate (2018-19) of Area and Production of various Horticulture Crops.
- As per the report, the total horticulture production in the country is estimated to be 313.85 million tonnes which is 0.69% higher than the horticulture production of 311.71 million tonnes in 2017-18.
- The area under horticulture crops has increased to 25.49 million hectares in 2018-19 from 25.43 million hectares in 2017-18.
The Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare (DAC&FW) is one of the three constituent departments of the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, the other two being Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries (DAHD & F) and Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE)
The Future prospects of Horticulture in India
- The horticulture sector as a diversified function of the agriculture sector has become a promising source of income opportunities. It contributes towards a steady growth for the sector as well as for the economy.
- India has evolved as a leading producer of horticulture products and emerged as a reliable source for employment generation, income creation, and export promotion.
- India is likely to gain a prominent place in the world forum with the help of better resource allocation, infrastructure development, technological upgrade, and better policy implementation for the development of the horticulture sector.
What can be done further to enhance the growth of the Sector?
A conscious effort is required to implement certain initiatives that would lead to the future growth and development of the horticulture sector. Some of the future initiatives are mentioned as follows:
- Import of technologies to improve the productivity and skill development in the horticulture sector.
- Application of organic farming methods in horticulture to achieve environmental and economic benefits in the production process.
- Adoption of more standardized processes in horticulture production that help farmers to apply knowledge and skills effectively towards improving production.
- The involvement of more private firms in the horticulture sector can bring more efficiency and export opportunities.
- The government should promote organic horticulture production by encouraging farms with incentives and providing support during the conversion from conventional to organic farming.
- Encourage farmers to adopt Good Agriculture Practices (GAP) by providing certifications. These practices help in producing fruits and vegetable products with improved quality. This in turn will generate more demand from foreign countries and boost export activities.
Agencies assciated
Indian Institute of Horticultural Research
- The Indian Institute of Horticultural Research(IIHR) is an autonomous organization acting as a nodal agency for basic, strategic, anticipatory and applied research on various aspects of horticulture such as fruits, vegetable, ornamental, medicinal and aromatic plants and mushrooms in India.
- The institute has its headquarters in Bengaluru, Karnataka, India and is a subsidiary of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi, under the Ministry of Agriculture.
- The Institute is mandated to:
- Undertake basic and applied research for developing strategies to enhance productivity and utilization of tropical and sub-tropical horticulture crops viz., fruits, vegetables, ornamentals, medicinal and aromatic plants and mushrooms.
- Serve as a repository of scientific information relevant to horticulture.
- Act as a centre for training for up gradation of scientific manpower in modern technologies for horticulture production.
- Collaborate with national and international agencies in achieving the above objectives.
National Horticulture Mission
- National Horticulture Mission(NHM) is an Indian horticulture Scheme promoted by Government of India.
- It was launched under the 10th five-year plan in the year 2005-06.While Government of India contributes 85%, 15% share is contributed by State Governments.
- The NHM's key objective is to develop horticulture to the maximum potential available in the state and to augment production of all horticultural products (fruits, vegetables, flowers, coco, cashew nut, plantation crops, spices, medicinal aromatic plants) in the state. Other objectives include:
- To provide holistic growth of the horticulture sector through an area based regionally differentiated strategies
- To enhance horticulture production, improve nutritional security and income support to farm households
- To establish convergence and synergy among multiple on-going and planned programmes for horticulture development
- To promote, develop and disseminate technologies, through a seamless blend of traditional wisdom and modern scientific knowledge
- To create opportunities for employment generation for skilled and unskilled persons, especially unemployed youth.
Benefits of Horticulture for India
- It contributes as the major source of Food and Nutrients.
- Sector provides large employment opportunities for such a large population in India.
- Horticultural products are mainly exported to the foreign countries and become an identity for India in foreign market.
- Contribution to GDP: It also adds foreign bullion the Economy.
- For Environmental sustainability, the production of inter-crop production or mixed cropping has proved to be beneficial for soil health.
- Source of herbal medicines- They are source of medicines obtained from the medicinal plants.
- As a raw material for food processing industries.
Challenges faced by Horticulture
- Inadequate availability of planting materials
- Rein-fed horticulture
- dearth of market facility
- Post-harvest management
- lack of processing facilities
- Insufficient trained manpower
Conclusion
“Green is good but it should be sustainable too.”
India is among the top producers of fruits and vegetables worldwide and is considered one of the best performers in horticulture production across the globe. The horticulture sector can experience further growth and profitability through improved techniques for production, farm mechanization to increase harvesting and processing efficiency, and procurement of best quality planting materials to produce high-quality products, but not at the cost of deteriorating the Environment and Health.



